

 All payments are encrypted via SSL
All payments are encrypted via SSL
 Full Refund if you haven't received your order
Full Refund if you haven't received your order
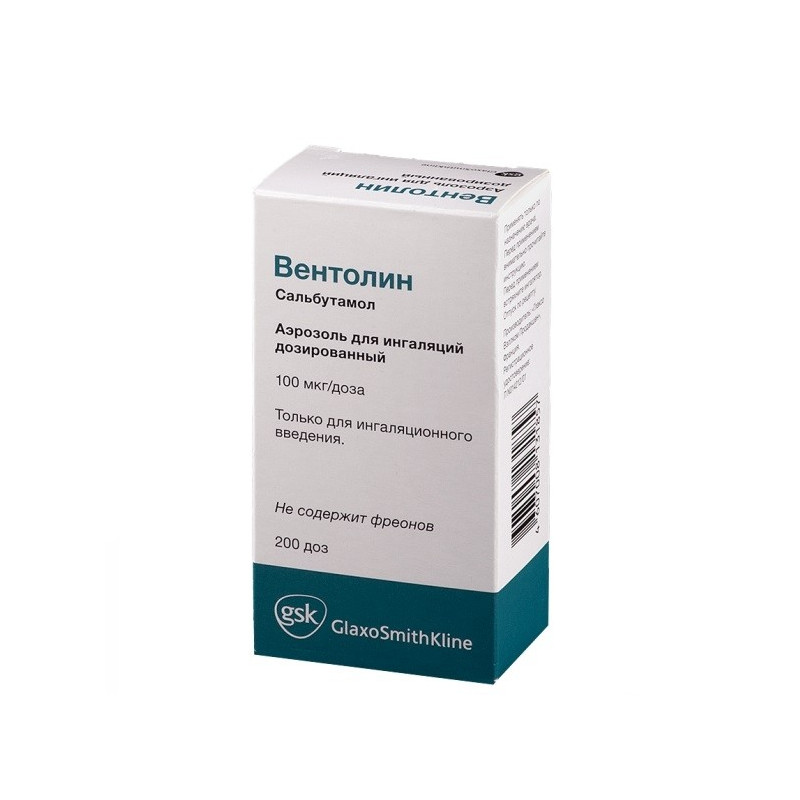
Dosed aerosol for inhalation
1 dose of Ventolin contains 100 mcg of Salbutamol (in the form of salbutamol sulfate).
Cylinder 200 doses.
Salbutamol is a b2-adrenoreceptor selective agonist. At therapeutic doses, Ventolin acts on the b2-adrenoreceptors of the smooth muscles of the bronchi, having little or no effect on the b1-adrenoreceptors of the myocardium.
Bronchial asthma
- relief of attacks of bronchial asthma, including the exacerbation of severe asthma;
- prevention of attacks of bronchospasm associated with exposure to an allergen or caused by exercise;
- use as one of the components for long-term maintenance therapy of asthma.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), accompanied by reversible airway obstruction, including chronic bronchitis and pulmonary emphysema.
- Hypersensitivity to any component of the drug Ventolin.
- Conducting preterm labor.
- Threatening abortion.
- Children's age up to 2 years.
During pregnancy and lactation, the drug Ventolin is prescribed only in cases where the expected benefit to the mother outweighs any possible risk to the fetus.
Salbutamol is likely to penetrate into breast milk, so nursing women are not recommended to take it, except in cases where the expected benefit to the mother outweighs any potential risk to the baby. It is not known whether Ventolin has any negative effect on a newborn baby that is present in breast milk.
Ventolin dosed aerosol is intended only for inhalation.
Only a doctor can decide whether to increase the dose or frequency of use of the drug Ventolin.
It is not recommended to use the inhaler Ventolin more often 4 times a day. The need for frequent use of maximum doses of Ventolin or in a sudden increase in dose indicates a worsening course of the disease.
Adults (including elderly patients)
Relief of bronchospasm: The recommended dose of ventolin is 100–200 mcg (1–2 inhalations).
Preventing attacks of bronchospasm, associated with exposure to an allergen or caused by exercise: the recommended dose of Ventolin is 200 mcg (2 inhalations) 10-15 minutes before exposure to a provoking factor.
Long-term maintenance therapy: The recommended dose is up to 200 mcg (2 inhalations) 4 times a day.
Ventolin can be administered via the Volumatik spacer.
Children
Relief of bronchospasm: The recommended dose of ventolin is 100–200 mcg (1–2 inhalations).
Preventing attacks of bronchospasm, associated with exposure to an allergen or caused by exercise: the recommended dose is 100–200 mcg (1–2 inhalations) 10–15 min before exposure to a provoking factor.
Long-term maintenance therapy:The recommended dose of Ventolin is up to 200 mcg (2 inhalations) 4 times a day.
Ventolin can be entered through the 'Babihaler' or 'Volumic' spacer.
Ventolin can cause mild tremor of skeletal muscles, which is usually most pronounced in the hands and is a characteristic side effect of all b2-adrenoreceptor agonists. Occasionally, patients have headache, dilated peripheral vessels and a slight compensatory increase in heart rate. Very rarely, hypersensitivity reactions (including angioedema, urticaria, bronchospasm, hypotension and collapse), muscle cramps, tachycardia develop.
Inhalation drugs can cause paradoxical bronchospasm. Paradoxical bronchospasm should be stopped immediately with another dosage form of salbutamol or another fast-acting inhaled bronchodilator. It is necessary to immediately discontinue the use of the Ventolin inhaler, evaluate the patient's condition, carry out the necessary examination and prescribe the appropriate therapy.
Inhalation drugs may cause irritation of the oral mucosa and pharynx.
Therapy with beta2-adrenoreceptor agonists sometimes causes hypokalemia, which can be a serious danger to the patient.
Like other beta2-adrenoreceptor agonists, Ventolin can occasionally cause mental stimulation and increased motor activity in children.
In patients with a predisposition to develop arrhythmias, Ventolin can cause cardiac arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, and extrasystole.
Patients should be instructed in the proper use of the Ventolin Inhaler.
Bronchodilators should not be the only or main component of the therapy of unstable or severe asthma.
If the effect of the usual dose of Ventolin becomes less effective or less prolonged (the effect of the drug should last at least 3 hours), the patient should consult a doctor.
The increased need for the use of inhaled β2-adrenoreceptor agonists with a short duration of action to control the symptoms of bronchial asthma indicates an exacerbation of the disease. In such cases, the patient’s treatment plan should be reviewed. A sudden and progressive worsening of bronchial asthma can pose a threat to the patient's life, therefore in such situations it is necessary to urgently decide on the appointment or increase in the dose of glucocorticosteroids. In such patients, daily peak expiratory flow rate monitoring is recommended.
Very high doses of Ventolin can lead to the development of adverse reactions, so only a doctor can decide whether to increase the dose or frequency of use of the drug. Patients who use Ventolin Nebula at home should be warned that if the effect of the usual dose becomes less effective or less prolonged, it is impossible to independently increase the dose or frequency of drug administration, and you should immediately consult a doctor.
Ventolin Nebula should be used with caution in patients who have already taken high doses of other sympathomimetics.
Ventolin should be used with caution in patients with thyrotoxicosis.
Therapy with β2-adrenoreceptor agonists, especially when administered parenterally or with a nebulizer, can lead to hypokalemia. Particular caution is recommended when treating severe attacks of bronchial asthma, since in these cases hypokalemia may increase as a result of the simultaneous use of xanthine derivatives, glucocorticosteroids, diuretics, and also due to hypoxia. In such situations, it is necessary to control the level of potassium in the serum.
It is not recommended to use Ventolin and non-selective b-adrenoreceptor blockers, such as propranolol, at the same time.
Salbutamol is not contraindicated in patients who receive monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
In case of an overdose of Ventolin, the best antidotes are cardio-selective b-blockers. However, b-adrenoreceptor blockers should be used with caution in patients with a history of bronchospasm. The use of large doses of salbutamol can cause hypokalemia, therefore, if overdose is suspected, the level of serum potassium should be monitored.
Store Ventolin at temperatures below 30 ° C.
