

 All payments are encrypted via SSL
All payments are encrypted via SSL
 Full Refund if you haven't received your order
Full Refund if you haven't received your order
One capsule of Madopar "125" (pink-blue) contains:
Levodopa 100 mg, benserazide 25 mg
One high-speed (dispersible) pill Madopar "125" (white)
contains: levodopa 100 mg, benserazide 25 mg
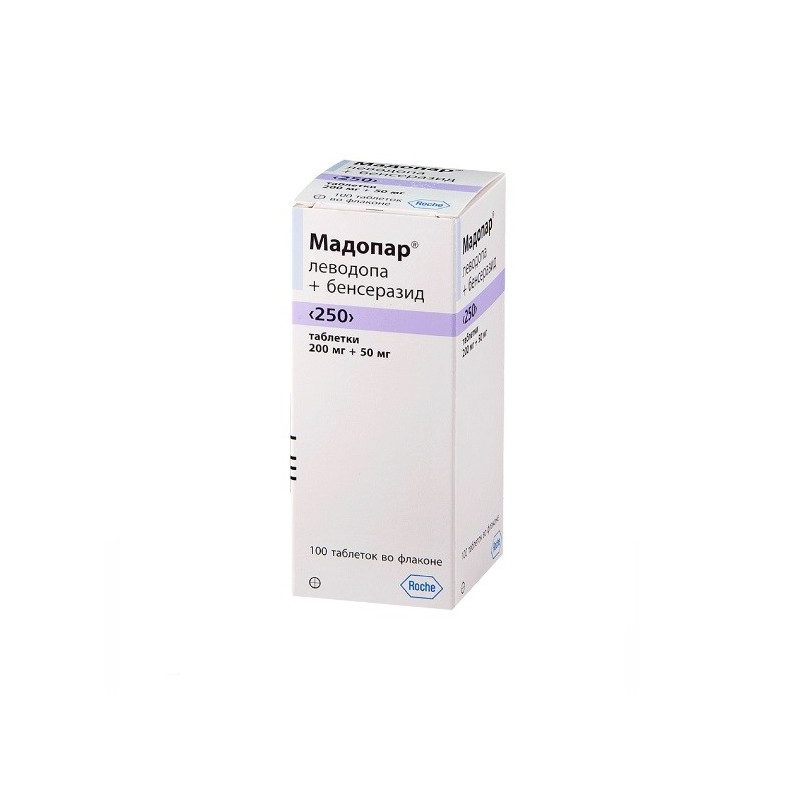
One pill Madopar "250" (pink) contains:
levodopa 200 mg, benserazide 50 mg
One capsule of Madopar GSS (hydrodynamically balanced system) (green-blue) contains:
Levodopa 100 mg, benserazide 25 mg
Fillers: dyes (depending on the form of release - indigotin (E 132), titanium dioxide (E 171) or iron oxide (E 172)).
Madopar "125": 30 or 100 capsules in a bottle.
Madopar high-speed pills (dispersible) "125": 30 or 100 pills per vial.
Madopar "250": 100 pills in a bottle.
Madopar GSS "125": 30 or 100 capsules in a bottle.
Madopar GSS capsules can not be opened before use, otherwise the effect of continuous, controlled release of the active substance is lost!
Anti-parkinsonic agent (dopamine precursor + decarboxylase peripheral inhibitor) [NO4BA]
Combined anti-parkinsonian
Dopamine, which is a neurotransmitter in the brain, is formed in the basal ganglia in patients with parkinsonism in insufficient quantities. Replacement therapy is carried out by prescribing levodopa, a direct metabolic precursor of dopamine, since the latter does not penetrate well.
across the blood-brain barrier.
After ingestion, levodopa rapidly decarboxylates to dopamine in both cerebral and extracerebral tissues. As a result, most of the injected levodopa does not reach the basal ganglia, and peripheral dopamine often causes side effects. Blocking extracerebral decarboxylation of levodopa is therefore highly desirable. This is achieved by the simultaneous administration of levodopa and benserazide, an inhibitor of peripheral decarboxylase.
Madopar is a combination of these substances in the 4: 1 ratio, which proved to be optimal in clinical trials and in medical practice and has the same efficacy as large doses of levodopa.
High-speed (dispersible) Madopar pills are especially indicated for patients with dysphagia (impaired swallowing), as well as patients who need a more rapid onset of action of the drug, for example, with akinesia in the early morning hours and in the afternoon, or for patients with the phenomenon of "slow start" and "The phenomenon of the end of the dose."
GSS capsules are a special dosage form that gives a slow release of active substances in the stomach, where the capsule remains from 3 to 6 hours, thus serving as a reservoir of the drug.
Parkinsonism.High-speed Madopar - a special dosage form for patients with dysphagia (swallowing disorders) and those cases when a more rapid onset of action is required, that is, for patients
with akinesia in the early morning hours and in the second half of the day, as well as for patients with the phenomenon of "delay" or "shutdown".
Madopar GSS is indicated for patients with any type of oscillation of the action of levodopa (namely, “dyskinesia of peak dose” and “end-of-dose phenomenon”, for example, stillness at night).
Treatment with Madopar should be started gradually, individually selecting the dose and bringing their effect to the optimum. The following dosing guidelines should therefore be understood as general guidelines.
Patients should always swallow the usual capsules of Madopar or Madopara GSS completely, without chewing. Conventional Madopar tablets, in contrast, can be crushed to facilitate swallowing.
High-speed pills Madopar need to be dissolved in a quarter cup of water (25-50 ml). The pill is completely dissolved in a few minutes with the formation of a milky white solution. Since precipitate can form quickly, it is recommended to stir the solution before taking it.
High-speed Madopar should be taken no later than half an hour after dissolving the tablet. Madopar should be taken, if possible, not less than 30 minutes before or 1 hour after a meal.
Initial treatment
Patients at an early stage of Parkinson's disease are advised to begin treatment with Madopar from taking 50 mg of levodopa + 12.5 mg of benserazide 3-4 times a day. As soon as the tolerance of the initial dosing regimen is confirmed, the dose should be slowly increased depending on the response of the patient.
The optimum effect is achieved, as a rule, with a daily dose of 300-800 mg of levodopa + 75-200 mg of benserazide, taken in three or more doses. It may take 4 to 6 weeks to achieve the optimum effect. If necessary, a further increase in the daily dose should be done at intervals of 1 month.
Supportive treatment
The average maintenance dose is 125 mg Madopar 3-6 times a day. The number of doses (at least three) and their distribution during the day should be determined so as to ensure the optimal effect. To optimize the effect, it may be necessary to replace conventional Madopar with dispersible
or Madopar GSS.
Dosing in special cases
Patients taking other anti-parkinsonian drugs can also receive Madopar. However, with the continuation of treatment with Madopar and the manifestation of its therapeutic effect, it may be necessary to reduce the dose of other drugs or their gradual elimination.
If during the day the patient experiences strong fluctuations in the action of the drug (the “on / off” phenomenon), it is recommended to either take more frequent, respectively, smaller single doses, or — preferably, use Madopar GSS.
The transition to Madopar GSS is best done from one day to another, starting with the morning dose.You should leave the same daily dose and regimen as the usual Madopar.
After 2-3 days, the dose is gradually increased by about 50%. Patients should be warned that their condition may temporarily worsen. Because of its features, the GSS Madopar begins to act somewhat later. The clinical effect can be achieved faster by prescribing GHL Madopar along with conventional capsules or Madopar high-speed tablets. This may be particularly useful in the case of the first morning dose, which should be somewhat higher than the next. The individual dose of Madopar GSS should be selected slowly and carefully, and the interval between dose changes should be at least 2-3 days.
In patients with nocturnal symptomatology, a positive effect was achieved by gradually increasing the evening dose to 250 mg of Madopar GSS before going to bed.
With a pronounced effect of Madopar GSS (dyskinesia), it is advisable to increase the intervals between doses, rather than reduce a single dose.
If Madopar GSS is not effective enough even in a daily dose corresponding to 1500 mg of levodopa, it is recommended to return to the previous treatment with conventional Madopar and Madopar fast-acting tablets.
Hypersensitivity to levodopa, benserazide or drug fillers. Madopar should not be prescribed together with non-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAO). However, selective MAO-B inhibitors, such as
selegiline, and selective MAO-A inhibitors, such as moclobemide, are not contraindicated. The combination of MAO-A and MAO-B inhibitors is equivalent to non-selective suppression of MAO, therefore such a combination cannot
to appoint simultaneously with Madopar (see the section "Drug Interactions").
Madopar should not be prescribed to patients with decompensated endocrine dysfunction, liver or kidney, diseases of the cardiovascular system, mental diseases with a psychotic component and angle-closure glaucoma. Madopar should not be prescribed to patients younger than 25 years (the development of the skeleton should be completed).
Madopar should not be prescribed to pregnant women or women of childbearing age who do not use reliable methods of contraception. If pregnancy occurs during treatment with Madopar, the drug should be immediately discontinued.
Anorexia, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, isolated cases of loss or change in taste. These side effects, possible at the initial stage of treatment, can be largely eliminated if Madopar is taken with food or with sufficient amount of food or liquid, and also if the dose is increased slowly. In rare cases - skin reactions in the form of itching and rash. Sometimes - arrhythmias or ortho-static hypotension. Orthostatic disturbances usually subside after reducing the dose of Madopar.
There are reports of rare cases of hemolytic anemia, as well as transient leukopenia and thrombocytopenia.Therefore, for any long-term treatment with levodopa, it is necessary to periodically determine the blood formula and monitor the function of the liver and kidneys.
In the later stages of treatment, spontaneous movements sometimes occur (for example, such as chorea or athetosis). They can usually be eliminated or reduced to an acceptable level by reducing the dose. With prolonged use of the drug, its therapeutic efficacy may vary. it
manifested in episodes of "freezing", weakening the effect by the end of the period of the dose and the phenomenon of "on-off". Usually, these phenomena can be eliminated or significantly reduced by reducing the dose or prescribing the drug at a lower dose, but more often. Subsequently, you can try again to increase the dose to enhance the effect of treatment.
In patients with old age, as well as in the presence of similar disorders in the history, agitation, anxiety, insomnia, hallucinations, delusions and temporary disorientation may be observed. When treating Madopar, depression can occur, although it can also be a manifestation of the underlying disease.
Sometimes a transient increase in the activity of hepatic transaminases and alkaline phosphatase may develop. In patients receiving Madopar (levodopa), there was an increase in blood urea nitrogen. The color of urine may change, usually up to red, darkening when standing.
Persons with hypersensitivity may develop appropriate reactions.
Patients with open-angle glaucoma are recommended to regularly measure intraocular pressure, since in theory levodopa can increase intraocular pressure.
In the course of treatment, it is necessary to check the function of the liver and blood formula.
Patients with diabetes often need to monitor their blood sugar levels and, in accordance with them, change the dose of antidiabetic drugs.
If possible, taking Madopar should be stopped 12-48 hours before surgical interventions that require general anesthesia (except for emergency cases), since a patient receiving Madopar may experience fluctuations in blood pressure and arrhythmias during halothane anesthesia. After surgery, treatment is resumed, gradually increasing the dose to the previous level.
Madopar can not be canceled abruptly. Abrupt withdrawal of the drug can lead to a "malignant neuroleptic syndrome" (fever, muscle rigidity, as well as possible mental changes and an increase in serum creatine phosphoninase), which can take a life-threatening form. If such symptoms occur, the patient should be under the supervision of a physician (be hospitalized if necessary) and receive appropriate symptomatic therapy. It may include the reappointment of Madopar after appropriate assessment of the patient’s condition.
Patients should be carefully observed in terms of the possible occurrence of mental adverse reactions.
Pregnancy and lactation
Because of the possible developmental impairment of skeletal development in the fetus, Madopar is absolutely contraindicated in pregnancy and in women of childbearing age who do not take adequate
contraceptive measures.
Since it is not known whether benserazide passes into breast milk, then, if a nursing mother needs treatment with Madopar, she should stop breastfeeding, since this does not preclude the abnormal development of the skeleton of the child.
Pharmacokinetic interactions
The prescription of the anticholinergic drug trihexyphenidyl together with the usual Madopar reduces the rate, but not the degree of absorption of levodopa. The administration of trihexyphenidyl together with Madopar GSS does not affect the pharmacokinetics of levodopa.
Appointment of antacids together in Madopar GSS reduces the degree of absorption of levodopa by 32%.
Ferrous sulfate reduces the maximum concentration and AUC of levodopa in plasma by 30-50%; these changes in some (but not all) patients are clinically significant.
Metoclopramide increases the rate of absorption of levodopa.
Levodopa does not enter into pharmacokinetic interactions with Bromocriptine , amantadine, selegiline and Domperidone .
Pharmacodynamic Interactions
Neuroleptics, opiates and antihypertensive drugs containing reserpine, suppress the action of Madopar.
If it is decided to prescribe Madopar to patients receiving irreversible non-selective MAO inhibitors , at least two weeks should pass from discontinuing the MAO inhibitor before starting to receive Madopar (see the section "Contraindications").However, selective MAO-B inhibitors (such as lazabemide or selegilin) and selective MAO-A inhibitors (such as moclobemide) can also be prescribed during treatment with Madopar. It is recommended to adjust the dose of levodopa, depending on the individual needs of the patient in terms of effectiveness and tolerability. The combination of MAO-A and MAO-B inhibitors is equivalent to receiving a non-selective MAO inhibitor, therefore such a combination should not be administered simultaneously with Madopar.
Madopar should not be administered simultaneously with sympathomimetics (drugs such as adrenaline, norepinephrine, isoproterenol or amphetamine, which stimulate the sympathetic nervous system), since levodopa can potentiate their action. If simultaneous administration is nevertheless obligatory, close monitoring of the cardiovascular system is very important and, if necessary, reducing the dose.
sympathomimetics.
Combined use of the drug with other antiparkinsonian drugs (anticholinergic, amantadine, dopamine agonists) is allowed, but this may enhance not only desirable, but also undesirable effects. You may need to reduce the dose of Madopar or another drug. If a catechol-o-methyltransferase / COMT / inhibitor is added to the treatment, a reduction in the dose of Madopar may be required.
If treatment with Madopar is started, anticholinergic drugs should not be abolished abruptly, since levodopa does not begin to act immediately.
Levodopa may interfere with laboratory tests for catecholamines, creatinine, uric acid and glucose.
In patients receiving Madopar, Coombs test may give false positive results.
Taking the drug at the same time as high-protein food can interfere with the absorption of levodopa from the gastrointestinal tract.
The most common symptoms of an overdose are involuntary movements, confusion, insomnia, and less commonly nausea, vomiting, or arrhythmias. In case of overdose, it is recommended to immediately wash the stomach, as well as to establish observation of the respiratory function and cardiac activity. It may be necessary to prescribe respiratory analeptics and / or antiarrhythmic agents or, if appropriate, antipsychotics.
Madopar “125" capsules and pills - 3 years.
Madopar "250" pills - 4 years.
The drug should not be used beyond the expiration date printed on the package (EXP).
Madopar "125" capsules stored at temperatures up to 30 ° C.
Madopar pills "125" and "250" stored at temperatures up to 25 ° C.
Keep out of the reach of children
It is released on prescription.
Madopar