


 All payments are encrypted via SSL
All payments are encrypted via SSL
 Full Refund if you haven't received your order
Full Refund if you haven't received your order
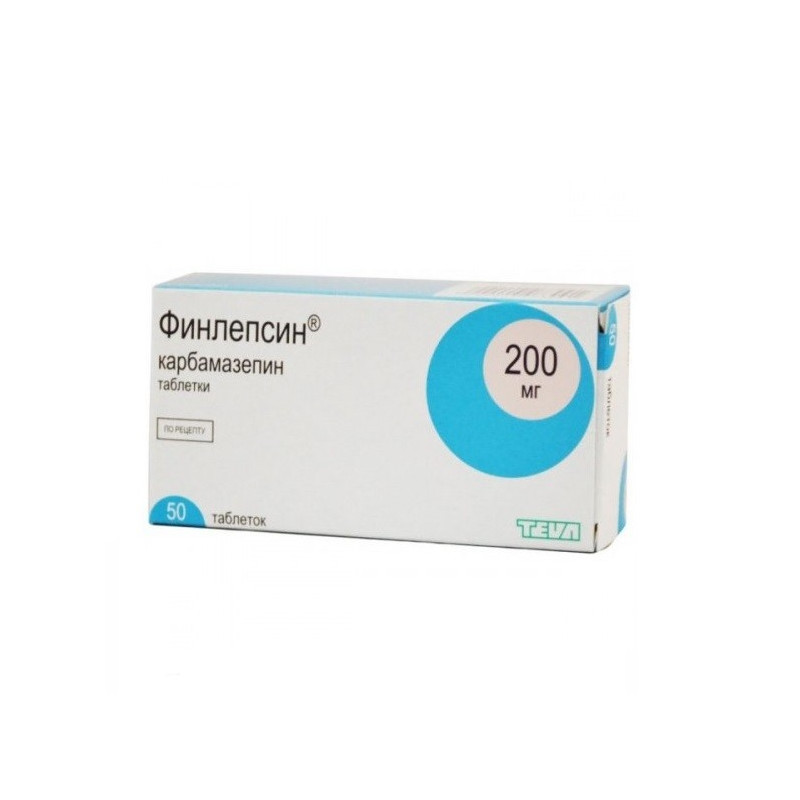
FINLEPSIN tAbletki: 1 pill contains Carbamazepine 200 mg;
Excipients: gelatin, Magnesium stearate; MCC, croscarmellose sodium;
10 pieces. in a blister, 5 blisters in a carton box..
long acting tablets from white to white with a yellowish tint, round flat pills with beveled edges, on one side a cross-shaped incision, on the other - engraving “C 200” (200 mg) or “C 400” (400 mg).
1 pill contains carbamazepine 200 or 400 mg;
Excipients: ammonium methacrylate copolymer type B (contains sorbic acid and sodium hydroxide); glycerol triacetate; talc; methacrylic acid - ethyl acrylate copolymer (contains sodium lauryl sulfate and polysorbate 80); MCC; crospovidone; colloidal anhydrous silica; magnesium stearate;
10 pieces. in a blister, 5, 10, 20 blisters in a carton box.
Antiepileptic drug, whose action is associated with a decrease in the ability of neurons to maintain a high frequency of development of repeated action potentials through inactivation of sodium channels. In addition, it seems to be important to inhibit the release of neurotransmitters by blocking presynaptic sodium channels and the development of action potentials, which in turn reduces synaptic transmission.
The drug has a moderate anti-manic, antipsychotic effect, as well as an analgesic effect for neurogenic pain.
- epilepsy: partial seizures with both simple and complex symptoms; generalized tonic-clonic convulsions, mainly of focal genesis (large seizures during sleep, diffuse large seizures); mixed forms of epilepsy;
- alcohol withdrawal syndrome (used in the hospital);
- neuralgia: trigeminal neuralgia; glossopharyngeal neuralgia; pain syndrome in diabetic neuropathy;
- epileptiform painful convulsions in multiple sclerosis (for example, facial muscles in the trigeminal neuralgia); tonic convulsions; paroxysmal dysarthria and ataxia; paroxysmal paresthesias and bouts of pain;
- psychosis (especially manic-depressive psychosis, anxiety-agitated and hypochondriacal depression, catatonic arousal).
Set individually, taking into account the indications and the patient's condition.
For adults prescribed in the initial daily dose of 200-300 mg; then the dose is gradually increased to 600 mg-1.2 g / day. The multiplicity of appointment is 3-4 times / day.
Patients with severe diseases of the cardiovascular system, liver and kidneys, and elderly patients the drug is prescribed in lower doses.
For children The average maintenance dose is 10–20 mg / kg body weight / day.
The following dosing regimen is recommended:
| Patients | Initial dose | Maintenance dose |
|---|---|---|
| Children from 6 to 10 years | 200 mg in the evening | 200 mg in the morning and 200-400 mg in the evening |
| Children from 11 to 15 years | 150-200 mg in the evening | 200-400 mg in the morning and 400-600 mg in the evening |
| Adults | 200-300 mg in the evening | 200-600 mg in the morning and 400-600 mg in the evening |
Epilepsy has been treated for years. Reduce the dose of the drug or cancel it only after a 2-3-year absence of seizures. Treatment is stopped by gradually lowering the dose of the drug within 1-2 years.
To prevent the development of convulsive seizures in the syndrome of alcohol withdrawal in the hospital the drug is prescribed in an average daily dose of 200 mg in the morning and 400 mg in the evening. In severe cases, in the first days of treatment, the daily dose can be increased to 1.2 g. Treatment is stopped by gradually reducing the dose for 7-10 days. During treatment, it is necessary to regularly monitor the level of carbamazepine in the blood plasma.
In trigeminal neuralgia and glossopharyngeal neuralgia the drug is prescribed in the initial dose of 200-400 mg / day. This dose is increased up to the complete disappearance of pain to 400-800 mg / day, which is divided into 1-2 doses. After this treatment, you can continue with a maintenance dose of 400 mg / day and divided into 2 doses.
Pin pain syndrome in diabetic neuropathy The average daily dose is 200 mg in the morning and 400 mg in the evening. In exceptional cases, you can assign up to 1.2 g / day.
In epileptiform convulsions in multiple sclerosis the average daily dose is 400-800 mg, divided into 2 doses.
For the treatment and prevention of psychosis the drug is prescribed in a dose of 200-400 mg / day. If necessary, this dose can be increased to 800 mg / day.
Patients with severe diseases of the cardiovascular system, liver and kidneys, as well as elderly patients, are prescribed the drug in lower doses.
Tablets of prolonged action should be taken with or after a meal, drinking plenty of liquids. pills of prolonged action can be taken after their preliminary dissolution in water (in the form of suspension).
Nervous system: mainly at the beginning of treatment may be headaches, dizziness, visual disturbances, drowsiness, ataxia; in elderly patients, confusion and anxiety are also possible; rarely - speech disorders, involuntary movements, paresthesias, muscle weakness, hallucinations, depressed mood, lethargy, decreased activity, aggressive behavior.
Cardiovascular: bradycardia, AV block; rarely, arterial hypo or hypertension; in some cases - thromboembolism.
Gastrointestinal: nausea, vomiting are possible; rarely - diarrhea, constipation, increased activity of hepatic transaminases; in some cases - jaundice, hepatitis.
Hemic and lymphatic: rarely - anemia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia.
Allergic reactions: rarely - pruritus, rash, urticaria, Lyell's syndrome, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Dermatologic: in some cases - photosensitivity, purpura, alopecia, increased sweating, disseminated lupus erythematosus.
Respiratory: in some cases - pneumonitis, shortness of breath.
Urogenital: in some cases - interstitial nephritis, renal failure, albuminuria, hematuria, oliguria, dysuria.
Other: rarely - hyponatremia, edema, weight gain; in some cases - conjunctivitis, lymphadenopathy, galactorrhea, gynecomastia, sexual dysfunction.
- disorders of bone marrow hematopoiesis;
- AV blockade (except for patients with an artificial pacemaker);
- simultaneous administration of MAO inhibitors;
- simultaneous administration of lithium preparations;
- Hypersensitivity to carbamazepine and tricyclic antidepressants.
Due to the large amount of active ingredient and insufficient experience accumulated when using pills of prolonged action, the drug in the form of pills of prolonged action of 200 mg and 400 mg is not recommended for children under 6 years of age. This category of patients is recommended to prescribe pills of non-prolonged action.
The use of Finlepsin during pregnancy is possible only for health reasons. If it is necessary to prescribe a pregnant woman with anticonvulsant therapy, monotherapy should be carried out with a single drug, avoiding the use of combinations.If necessary, the use of the drug in the early stages of pregnancy (especially between 20 and 40 days) should be applied minimum doses of Finlepsin.
If necessary, the use of Finlepsin in a nursing mother should consider whether to continue breastfeeding. In case of poor weight gain or increased excitability of the infant, breastfeeding should be stopped.
The drug is not prescribed for small epileptic seizures.
Caution should be exercised in the appointment of Finlepsin to patients with blood diseases; severe diseases of the cardiovascular system, liver and kidneys; severe violations of water and electrolyte metabolism.
When treatment with Finlepsin, there is a risk of activation of latent endogenous psychosis, therefore, prior to treatment, a history should be studied and the patient’s mental status should be investigated.
Alcohol should not be taken during Finlepsin treatment.
During treatment with Finlepsin, changes in blood concentration T are possible.3T4, TSH.
Acceptance of MAO inhibitors should be completed no later than 2 weeks before the start of treatment with Finlepsin.
Influence on ability to drive motor transport and control mechanisms
Patients taking Finlepsin should refrain from potentially dangerous activities that require increased attention and quickness of psychomotor reactions (driving a car, working with moving machinery).
Symptoms: dizziness, ataxia, stupor, nausea, vomiting, anxiety, confusion, involuntary movements, mydriasis, nystagmus, heat sensation, urinary retention, cyanosis, opisthotonus, weakening or increasing reflexes, tremor, agitation, tonic-clonic convulsions, and respiratory disorders , arterial hypotension (sometimes hypertension), tachycardia, AV block, up to the cessation of breathing and the heart.
Treatment: there is no specific antidote. Conduct gastric lavage or artificially induce vomiting, prescribe activated charcoal, laxatives. Next, carry out symptomatic therapy aimed at maintaining the function of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. When convulsive seizures develop, other anticonvulsants, other than barbiturates, are prescribed because of their depressant effect on breathing. Forced diuresis, hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis are not very effective.
With the simultaneous use of Finlepsin and other anticonvulsants (for example, difenina, phenobarbital), mutual anticonvulsant action is possible, and in rare cases - its strengthening.
With the simultaneous use of Finlepsin and valproic acid in rare cases may develop confused consciousness and coma.
With the simultaneous use of Finlepsin reduces the effect of indirect anticoagulants, hormonal contraceptives.
With the simultaneous use of Finlepsin and lithium preparations, mutual enhancement of the effect on the central nervous system is possible.
With simultaneous use with Tetracycline , the effects of Finlepsin may be reduced.
With the simultaneous use of Finlepsin and Erythromycin , isoniazid, Verapamil , diltiazem, dextropropoxyphene, viloxazine and cimetidine may increase the concentration of carbamazepine in the blood.
The drug should be stored at room temperature.